While online learning such as Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) have been a boon to students, it comes at the cost of posing unique assessment challenges to teachers who offer these courses to a large class of students. These challenges are further compounded in graduate-level courses dealing with advanced topics that require individual original work to ensure that the learning objectives are met and typically they involve a course project.


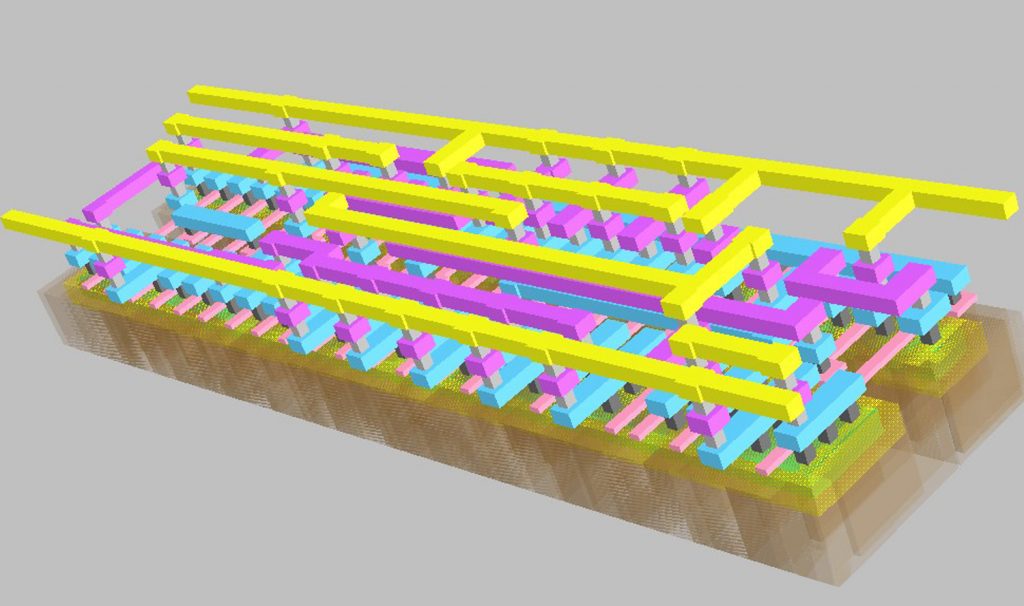
In this paper, the authors which include Mr. Alfred Festus Davidson from the Department of Electrical Engineering, Columbia University, New York, USA, and Prof. Janakiraman Viraraghavan from the Department of Electrical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras, Chennai, India, have focused on the design of the Digital Integrated-Circuit (IC) Design course for large classes. The students are exposed to the idea of a circuit layout for the first time and hence the course structure allows handholding, through Teaching Assistants (TAs), in the initial assignments and rapidly builds up to a non-trivial project involving a few thousand transistors. Theory and practice proceed in lock step allowing the students to appreciate and reinforce what has been taught in the class. The TAs play a critical role in providing feedback to the students and improving the layout of their standard cells which in turn determine how efficient the final layout is. One of the key contributions of this paper is the introduction of a plagiarism tool that compares two layouts in the standard GDSII format and reports a fuzzy similarity index, which serves as a guide for human inspection. This is the first reported plagiarism detection tool for GDSII format.
It was found that the introduction of a course project translated to better performance and resulted in a marked increase in students meeting the learning objectives. The inclusion of layout-based design projects in the course gave students a better understanding of the physical nature of the design. In summary, a structure of assignments and projects that allowed layout-based design for large classes was detailed, along with consideration of tools, evaluation metrics, and plagiarism detection.
Dr. Viveka Konandur Rajanna from the Department of Electronic Systems Engineering, Indian Institute of Science (IISc) Bengaluru, India, appreciated the work done by the authors by giving the following comments: “The paper “Layout-Based Digital IC Course Projects in Large Classes: Implementation, Evaluation, and Plagiarism Detection” provides extensive coverage of aspects relevant to conducting an introductory course in digital VLSI circuits. Evaluations and assessment of learning objectives are important challenges, especially for large student numbers such as the instances mentioned in the paper. The proposed method of repurposing the layout XOR feature of tools to help identify instances of plagiarism is very interesting and useful – saving the instructors’ valuable time that may be better utilized to achieve the learning objectives. The described method has additional layers of verification which are important to “stay ahead of the curve”. The experimental evaluation, measuring the impact of the proposed method, across multiple batches of students helps illustrate the effectiveness in achieving the said objectives. I thank the authors for sharing their experiences which will help improve the impact of similar courses across many institutions!”
Article by Akshay Anantharaman
Here is the original link to the paper:
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9849476